In France, Le Monde newspaper published an opinion piece last week written by Pierre Bellanger, founder and president of commercial radio group Skyrock, and Sylvain Anichini, former director general of state-owned Radio France:
LET’S NOT MESS UP DIGITAL RADIO
The powers that be are asking themselves a question about the transition to digital radio - if digital terrestrial television is a success, why would the transition to digital terrestrial radio not be a similar success?
In reply, experts have suggested there are differences between digital television and digital radio. Digital television is nationally operated and is being introduced nationally, whereas digital radio is being planned region-by-region with no certainty for radio operators who must apply for digital spectrum. Digital television offers three times as many free channels as analogue, whereas digital radio offers only a marginal increase over the wide choice available on analogue. Digital television was launched with a new generation of TV receivers – flat screens and high definition – and with adaptors for existing equipment. This is not the case for digital radio – digital radio receivers are as sexy as bricks and 140 million analogue radios will have to be thrown away.
Furthermore, digital television launched just when the medium was exploiting new sources of advertising revenues – once the preserve of radio – and when purchasing power was growing in line with the economy. Whereas, the transition to digital radio is being implemented just as the radio industry is reeling from the 2008 financial crisis and household spending is in decline. Finally, the television sector received significant financial help to fund its digital switchover. For digital radio, the subject of funding has been mentioned, and even said to be desirable, but there has been no promise to date. Public funding is not there to support the public will.
These facts have not stopped the powers that be, who have promised to overcome these obstacles. Driven by legislation, they have proceeded towards the launch of digital radio by involving key radio industry players in their strategy to select both a digital radio transmission standard and the most appropriate waveband to use. Applications have been submitted by radio opertaors for the first digital radio areas and there will be a selection process, just as for analogue radio, with licences awarded to the candidates of choice.
This process involves a substantial number of declarations of intent as to the magic of ‘digital’ in a concept synonymous with modernity. Perhaps we are forgetting somewhat that the CD, also digital, belongs more to the past than to the future ….
We are where we are. At the moment of truth when ‘poetry’ must give way to number-crunching and it seems that national digital radio transmission will cost at least 3 million Euros per annum, adding up to a total 50 million Euros per annum for the main radio groups. Additional transmitters are likely to need to be added to alleviate pockets of poor reception. And the absence of real competition between transmission providers offers little hope of reducing these costs. Finally, no new tangible sources of radio advertising are anticipated, and broadcasting will begin without a significant body of digital radio receivers in the market …
This kind of investment – more than 250 million Euros over seven years – might be justified if it could be amortised over two future decades that offered technological and economic stability. But we presently live in the midst of a complete revolution: the emergence of mobile internet access. This offers consumers the ability to connect anytime, anywhere, without interruption, to the internet via the airwaves.
The logic of the mobile internet is redefining the physical distribution of information and is disrupting traditional media and telecoms. The fixed internet has already changed our present, and the mobile internet is opening up the future. Radio is fully participating in this mutation, with radio distribution adapting to the internet protocol with ‘IP radio’.
The future is already in our hands: it is the iPhone. This revolutionary handheld device has allowed the internet to break into the mobile environment via existing communications networks. It provides access to thousands of radio stations, personalised music choices, and the user’s own media library.
Access is either through telecoms networks or through free Wi-Fi available at home or from millions of free wireless terminals. The multi-standard chip lets us forget about having to make a choice between network connections. We click and listen to our favourite radio station, that is all there is to do. ‘IP radio’ offers every radio station that is available via a conventional transistor radio.
The internet handset is connected to the car radio, the home hi-fi, the radio alarm clock, and chips that connect us to the internet on the move will be everywhere.
Already one and a half million iPhones have been sold in France. An entire industry, in less than two years, has caught up with touchscreen technology and IP handsets. It is true that the bandwidth, like the handsets, remain expensive, and telecoms networks must gear themselves towards new demands, but the trend is there: prices will fall. Besides, on the horizon is a converged pricing structure combining fixed broadband and mobile internet access in a package that offers unlimited usage. Therefore, how can we possibly build a viable market for digital radio receivers when the replacement cycle for radios is ten years, whilst that for (subsidised) mobile handsets is 18 months?
Unlike digital terrestrial radio, there is a business model for radio delivered by IP – it allows listeners to demand and receive advertisements specifically tailored to specific audience needs. This is internet audio. Listening is measured in real time and advertising space is traded in virtual marketplaces. IP-delivered radio has produced an unprecedented explosion of creative initiatives, supported by new economic models suited to micro-enterprises – look at the success of Radio Paradise.
What had once been little but a visionary thought is now beginning to make headway as a global standard – mobile internet is the new deal. It is the antithesis of the existing strata of broadcast networks specific to each medium (radio, television). In the future fragile economic landscape, where the concerns of preserving energy and the environment are becoming priorities, can we continue as if nothing has happened?
Careful thought by the powers that be should lead them to take account of these facts and to re-focus their administrative processes which risk becoming bogged down without public subsidy. Why not consider better use of digital networks that already exist? Digital terrestrial television which already allows radio, for example? And, whatever the case with radio, promote mobile internet access in the broader context of migration to a ‘digital’ France.
The planned migration to digital terrestrial radio was not a mistake, but a ‘future of delays’ overtaken by a technological revolution which has surprised entire industries. Recognising this does not take anything away from those who have defended their point of view. A change of course is never a mistake when it allows you to avoid hitting the reefs.
[unabridged]
[This blog was discontinued 2013. Check my current blog: link at top of sidebar.] I am an independent media analyst based in London, specialising in the radio broadcast industry. I have created and implemented successful strategies for the radio sector over three decades, including: the launch/turnaround of large-scale commercial music broadcasters in the UK, Europe and Asia; investment advice to City media shareholders; and significant contributions to public policy on broadcasting
27 Sept 2009
19 Sept 2009
Digital radio in France: cold feet, no funding, sue the regulator
On 10 September, the French secretary of state responsible for the digital economy, Nathalie Kosciusko-Morzet, organised a seminar “Digital: investing now for tomorrow’s growth”. The objective was to lay out to the 1000 attendees the costs and opportunities necessary to create an integrated digital economy.
On 16 September, Jean-Luc Hees, head of state broadcaster Radio France, addressed the National Assembly’s Committee on Finance & Cultural Affairs. He told them that the broadcaster’s advertising revenues were forecast to decline in 2009 by 20 to 30% year-on-year (advertising comprises 8% of revenue, the remainder from the state). He said that the rollout of digital radio in 2010 would require adding 2m to 3m Euros to the budget.
Hees told the National Assembly: “We now know fairly well the timing of the introduction of digital terrestrial radio, with launches in the coming months in three areas – Paris, Marseille and Nice. …. Our goal is to achieve 95% coverage of France by the end of 2013, according to the CSA’s [France’s media regulator] schedule. …. We must understand that everything has a cost, and the impact on Radio France’s finances means that this house will have to fund dual transmission [analogue and digital] for some time. Analogue transmission presently costs Radio France 80m Euros per annum. The rollout of digital radio will entail additional costs and this is one of the things that require funding in our next budget. I want to emphasise this.”
Amongst commercial radio operators, opinions on digital radio appear increasingly ambivalent. Franck Lanoux, deputy director of NextRadioTV said that digital radio “will not affect 95% of radio listening. It’s hard to identify how digital radio will develop – the receivers do not exist, yet the broadcasters are being asked to make significant investments. Consumers have nothing to listen with.”
The publication mediasactu commented this week that digital radio in France has become ensnared in a quagmire and that reservations amongst commercial broadcasters are becoming stronger:
“After putting all their weight behind persuading the government to adopt the T-DMB standard for digital terrestrial radio in December 2007, which is now nearly two years ago, radio broadcasters, particularly those that are members of GRN [France’s Digital Radio Group] and the Bureau de la Radio [France’s newly created radio trade body comprising the four largest commercial owners], are much more dubious about the real chance of succeeding with the transition to digital radio. Although they were unwavering only a few months ago, now major national radio groups, along with SIRTI [the French broadcasting trade union] and the regional stations, seem determined to thwart digital radio, or at least seriously slow down its development. Angered by the CSA’s decision to only select a handful of new markets to launch digital radio, as well as the costs that will be inherent with dual transmission for several years, not to mention the CSA’s cancellation of applications for 16 of the first 19 areas designated for digital radio, the broadcasters are now showing real reluctance.”
“The [radio] sector, already suffering from its current lack of revenues, is still waiting for the financial aid promised by the government to fund the migration to digital radio. Now, it seems clear that the total cost of the implementation of digital radio will be made greater by the choice of the T-DMB standard by the Ministry of Culture, at the request of GRN, and that the rollout will be much more expensive than it would be for the DAB+ standard. Moreover, according to our sources, the major radio groups are now putting all their weight behind challenging the decision of the CSA about the channel composition of the first multiplexes in order to delay their launch and buy extra time. According to our sources, some have already initiated legal action against the CSA.”
At the government seminar on 10 September, CSA president Michel Boyon reportedly took the opportunity to try to ‘save’ digital radio, suggesting that part of a new significant loan raised by the French government should be allocated to the rollout of digital radio. But, as mediasactu commented:
“The problem is whether public funds can be used to finance the construction of radio networks intended to broadcast commercial stations. Will the public agree to fund not only a digital transmitter network for commercial radio, but also the purchase, at great expense, of receiver hardware that offers a range of stations almost identical to what is already offered on FM?”
Interviewed in Le Figaro, RTL president Christopher Baldelli said:
“The timetable [for digital radio] will be respected if the CSA believes it is right, but migration to digital terrestrial radio is not a matter of principle. It involves a different economic issue than digital television. One impact is higher transmission costs, at approximately 3m Euros per channel, costing us 12m Euros for the whole [RTL] network (RTL, RTL2, Fun Radio, RTL-L'Équipe). The economic difficulty must be taken into account. It is a matter for the radio groups, the CSA and the government. It will take a lot of consultation.”
As mediasactu concludes in its article:
“Overtaken by the internet, mobile phones and MP3 players, does digital terrestrial radio still stand any chance of seducing the general public?”
Labels:
commercial radio,
CSA,
DAB,
digital radio,
France,
Grant Goddard,
GRN,
radio,
radio industry,
radio numerique,
RTL,
SIRTI,
T-DMB
17 Sept 2009
The demand for DAB radio: where is it?
Most of the current debate on the challenges facing DAB radio seems to be focused on ‘supply side’ issues, such as upgrading existing DAB transmitters, making DAB radio receivers available in cars and the creation of another national DAB multiplex. Surprisingly little of the talk is about the ‘demand side’ issues facing the DAB platform. What are consumers demanding from DAB radio? And how great is that demand?
There are two types of consumer demand for DAB: the demand for content broadcast on the DAB platform, and the demand for DAB radio receiver hardware. The two are inextricably linked. Consumer demand for DAB hardware is largely a function of demand for DAB content. You will only want to buy a DAB radio if you believe there is something interesting enough to listen to on it. Let’s examine some of the available data on these two issues.
Consumer demand for DAB content
Nobody is going to be motivated to spend money on a DAB receiver for listening to the radio if the platform only offers the same content already available to them on analogue receivers. Therefore, it must be the exclusive digital-only content available on DAB (and other digital platforms) that will persuade consumers to both use the DAB platform and to purchase a DAB radio receiver.
So how dissatisfied are consumers by the radio content choices (the range of radio stations) available to them on existing analogue radio receivers? Ofcom research shows that 91% of adults are satisfied with the existing choice of radio stations offered to them (see chart below), a proportion that has risen in recent years. This demonstrates that dissatisfaction with existing radio provision is extremely low, making it very difficult for any new platform to attract a substantial audience by offering content that will gratify consumers’ few unsatisfied demands.
[In case you are wondering if the increasing satisfaction with radio stations might be a direct result of the exclusive digital-only stations already offered on the DAB platform, it is worth noting that only 3.9% of hours listened to radio are attributed to digital-only stations [RAJAR 2009 Q2].]
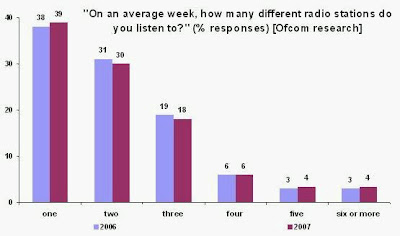
Ofcom data shows that the average consumer listens to very few radio stations. Two thirds of the population listen to only one or two different radio stations in an average week, and the majority of these two-thirds listen to only one station. So, not only are the overwhelming majority of consumers satisfied with their existing choice of radio stations, but most people listen to a very narrow menu of stations.
These phenomena are not the outcome of consumers only being offered a limited choice of radio stations on the analogue platform. Ofcom data demonstrates that, in addition to the 5 BBC radio stations and 3 commercial radio stations available nationally on analogue radio (with near universal coverage) in the UK, there are a significant number of local radio stations available to consumers in most areas of the UK. The average consumer in the UK has a choice of 8 national radio stations and 6 local radio stations.
This existing wide choice of radio stations makes the plan for migration to digital platforms very different for the radio medium than it is for the television medium. In the UK, only four (five in some areas) TV stations are available via analogue, making the wider choice available on digital platforms seem very attractive to consumers. Whereas, in radio, an average 14 stations are available to consumers on analogue, and these are already satisfying the vast majority of consumer demands. As a result, there is only a very tiny untapped consumer market for radio content not already available via analogue.
This is demonstrated by analysis of the largest UK radio market, London, in which consumer choice is at its greatest. There are 29 licensed radio stations available on the analogue platform in London (excluding community radio and out-of-area stations), but the top 3 stations account for just under a third of all radio listening in London, and the top 6 stations account for almost half of all radio listening. The radio market in London, as in most of the UK, is dominated by a tiny number of mainstream stations, whilst the remaining radio offerings comprise a ‘long tail’ that fulfils more specialist consumer needs.
The dramatic consumer skew towards mainstream radio means that, even in a radio market as developed as London, it proves difficult for incremental, digital-only stations to draw significant amounts of listening. The most listened to exclusively digital radio station in London is BBC 1Xtra, which ranks 22nd and attracts only a 0.5% share of listening in the market [RAJAR 2009 Q2]. 1Xtra’s content (UK black music) is barely duplicated by any other legal radio station available in London, and yet its ‘success’ remains slight in a very multicultural market that is already crowded with myriad radio options for consumers. The recent decision by London station Club Asia to enter administration, combined with the closures earlier this year of South London Radio and Time 106.8, demonstrate the challenge for stations to find a ‘monetisable’ audience in London, even on the analogue platform.
It might be easy to assume that Londoners, offered the widest selection of radio stations on the analogue platform, would be more satisfied with their choice in comparison with consumers in other, less well served parts of the UK. The surprising result from Ofcom research is that Londoners are, in fact, less satisfied with their choice of radio than most other parts of the UK. The chart below (extracted directly from a recent Ofcom report) demonstrates that satisfaction with existing radio provision is almost evenly spread across the whole UK, but consumers in London and Northern Ireland are the least satisfied.
In summary, radio in the UK has been a victim of its own success. The universal availability of a range of both BBC and commercial ‘national’ stations, combined with the extensive choice of local stations available in most markets, mean that consumers are already relatively spoilt for choice on the analogue radio platform. There is very little unsatisfied demand for radio content because the UK already has such a comprehensive choice of radio content on offer. As a result, any new radio platform (DAB, satellite, online, etc) is going to find it hard to compete with the high quality and diverse choice of what is already on offer.
This was always going to make it tough for the DAB platform to entice consumers to purchase DAB receivers as anything other than a ‘replacement’ for their existing analogue radios. Unfortunately, the natural replacement cycle for radio receivers is so slow (maybe ten years or more) that it will never prove sufficient for a complete UK digital switchover to be co-ordinated for radio, as is happening in the television market. The UK has some of the best radio in the world – ironically, this has been our digital downfall.
Consumer demand for DAB radio receivers
As noted earlier, consumer demand for DAB hardware is largely a function of demand for DAB content. You will only want to buy a DAB radio if there is something interesting enough you want to listen to on the DAB platform.
Ofcom research demonstrates clearly the lack of interest amongst consumers in purchasing DAB radio receivers. In this year’s survey, only 16% of consumers (without a DAB radio) say they are likely to purchase a DAB radio within the next 12 months. Two years ago, 19% said they would be likely to purchase a DAB radio within the next 6 months. This is very bad news for manufacturers and retailers of DAB radios. Worse, this year not only do 64% of consumers say they are unlikely to purchase a DAB radio, but 20% say they don’t know – a demonstration that a DAB radio is far from being a ‘must have’ gadget on consumers’ wants lists.
The data for current levels of DAB radio receiver ownership are not very helpful in determining the demand for DAB radio receivers. The quarterly survey by RAJAR found in 2009 Q1 that 32.1% of adult respondents claimed to own a DAB radio. However, the annual Ofcom survey found in the same quarter that 41% of adult respondents claimed to have a DAB radio in their household. This disparity between the results from RAJAR and Ofcom would appear to be widening over time.
The uncertainty in the data regarding ownership levels of DAB receivers is not surprising, given the evident level of consumer confusion. Firstly, many radios on the market have the words “digital” or “digital radio” written on them, meaning that they either incorporate a digital clock (for radio alarm clocks) or that they offer ‘digital’ tuning of analogue wavebands, despite them not offering DAB reception. Secondly, the majority of 'DAB radios' presently on sale in the UK offer DAB reception in combination with analogue radio and/or internet radio. When DAB radio receivers were first introduced a decade ago, all the models offered were DAB-only. Nowadays, it is harder to find a DAB-only model in shops. Earlier this year, I surveyed the radio hardware on sale from UK retailers (see chart below) and found that the most common DAB consumer proposition is now an ‘FM + DAB’ radio.
In its latest consumer research on take-up of digital radio, Ofcom said that the result of its survey (see below) “highlights the continued lack of awareness among consumers of ways of accessing digital radio”. Consumers have low awareness of their ability to already access digital radio, and It appears that the words “digital radio”, “digital audio broadcasting” and “DAB” are not yet precisely understood. This uncertainty makes the results of market research about ownership levels of DAB radio hardware somewhat unreliable.
One of the targets set by the Digital Radio Working Group at the end of 2008 for the implementation of digital radio was that DAB radios should reach 50% of radio receiver sales by volume by the end of 2010. However, if the current rate of growth continues, this target is unlikely to be reached until 2016 (see chart below).
Besides, this target is largely irrelevant to digital switchover because it seems to assume that consumers are making a definitive choice between the purchase of a DAB radio or an analogue radio. In fact, as the earlier chart shows, the majority of DAB radios presently offered by retailers also include FM radio. Although the DRDB data states that 22% of radios sold in the UK incorporate DAB, the vast majority of those include FM too. So, for every 100 new radios sold, you are probably adding to the UK’s inventory of receivers between 95 and 98 new FM radios, at the same time as adding 22 new DAB radios. In other words, the household penetration level of analogue radio receivers is barely diminishing at all, a fact that will ensure that FM broadcasting remains as vital to our radio system as it has always been.
In summary, the DAB platform seems to be developing slowly as a supplementary platform to existing analogue radio reception. Far from DAB radios ‘replacing’ analogue radios, the overwhelming majority of new radios purchased in the UK are still analogue-only. The remainder are mostly DAB/analogue combination receivers. In this way, DAB has much in common with ‘Long Wave’ radio, where consumers for a long time were offered a choice of ‘FM+AM’ or FM+AM+Long Wave’ receivers in retail stores. Like Long Wave, for a minority of consumers DAB may be a ‘must have’ when purchasing a new radio, but for the majority it is merely an optional extra whose purchase is likely to be very dependent on the comparative prices of available options.
Conclusion
The publicly available data on the demand for DAB is not particularly encouraging for the platform’s future. Much of the implementation of DAB to date in the UK has focused on ‘supply-side’ issues, without seeming to determine whether there is sufficient demand from consumers for new content, and without determining whether that new content would prove sufficiently attractive to lure consumers into shops to purchase DAB radios. Ironically, it appears that if our existing system of analogue radio broadcasting had been less well developed in terms of both the range of available content and its near universal delivery, DAB might have been better able to address any pent-up demand from consumers. As it is, the majority of consumers seem very content with their existing radio options. Our pursuit of excellence in radio over the last 80 years has created something we can be proud of – but it has also made it hard for it to be bettered by a ‘new’ system such as DAB.
[For more data on the challenges facing digital radio in the UK, check out a presentation I made to the European Broadcasting Union Digital Radio Conference in June 2009]
There are two types of consumer demand for DAB: the demand for content broadcast on the DAB platform, and the demand for DAB radio receiver hardware. The two are inextricably linked. Consumer demand for DAB hardware is largely a function of demand for DAB content. You will only want to buy a DAB radio if you believe there is something interesting enough to listen to on it. Let’s examine some of the available data on these two issues.
Consumer demand for DAB content
Nobody is going to be motivated to spend money on a DAB receiver for listening to the radio if the platform only offers the same content already available to them on analogue receivers. Therefore, it must be the exclusive digital-only content available on DAB (and other digital platforms) that will persuade consumers to both use the DAB platform and to purchase a DAB radio receiver.
So how dissatisfied are consumers by the radio content choices (the range of radio stations) available to them on existing analogue radio receivers? Ofcom research shows that 91% of adults are satisfied with the existing choice of radio stations offered to them (see chart below), a proportion that has risen in recent years. This demonstrates that dissatisfaction with existing radio provision is extremely low, making it very difficult for any new platform to attract a substantial audience by offering content that will gratify consumers’ few unsatisfied demands.
[In case you are wondering if the increasing satisfaction with radio stations might be a direct result of the exclusive digital-only stations already offered on the DAB platform, it is worth noting that only 3.9% of hours listened to radio are attributed to digital-only stations [RAJAR 2009 Q2].]
Ofcom data shows that the average consumer listens to very few radio stations. Two thirds of the population listen to only one or two different radio stations in an average week, and the majority of these two-thirds listen to only one station. So, not only are the overwhelming majority of consumers satisfied with their existing choice of radio stations, but most people listen to a very narrow menu of stations.
These phenomena are not the outcome of consumers only being offered a limited choice of radio stations on the analogue platform. Ofcom data demonstrates that, in addition to the 5 BBC radio stations and 3 commercial radio stations available nationally on analogue radio (with near universal coverage) in the UK, there are a significant number of local radio stations available to consumers in most areas of the UK. The average consumer in the UK has a choice of 8 national radio stations and 6 local radio stations.
This existing wide choice of radio stations makes the plan for migration to digital platforms very different for the radio medium than it is for the television medium. In the UK, only four (five in some areas) TV stations are available via analogue, making the wider choice available on digital platforms seem very attractive to consumers. Whereas, in radio, an average 14 stations are available to consumers on analogue, and these are already satisfying the vast majority of consumer demands. As a result, there is only a very tiny untapped consumer market for radio content not already available via analogue.
This is demonstrated by analysis of the largest UK radio market, London, in which consumer choice is at its greatest. There are 29 licensed radio stations available on the analogue platform in London (excluding community radio and out-of-area stations), but the top 3 stations account for just under a third of all radio listening in London, and the top 6 stations account for almost half of all radio listening. The radio market in London, as in most of the UK, is dominated by a tiny number of mainstream stations, whilst the remaining radio offerings comprise a ‘long tail’ that fulfils more specialist consumer needs.
The dramatic consumer skew towards mainstream radio means that, even in a radio market as developed as London, it proves difficult for incremental, digital-only stations to draw significant amounts of listening. The most listened to exclusively digital radio station in London is BBC 1Xtra, which ranks 22nd and attracts only a 0.5% share of listening in the market [RAJAR 2009 Q2]. 1Xtra’s content (UK black music) is barely duplicated by any other legal radio station available in London, and yet its ‘success’ remains slight in a very multicultural market that is already crowded with myriad radio options for consumers. The recent decision by London station Club Asia to enter administration, combined with the closures earlier this year of South London Radio and Time 106.8, demonstrate the challenge for stations to find a ‘monetisable’ audience in London, even on the analogue platform.
It might be easy to assume that Londoners, offered the widest selection of radio stations on the analogue platform, would be more satisfied with their choice in comparison with consumers in other, less well served parts of the UK. The surprising result from Ofcom research is that Londoners are, in fact, less satisfied with their choice of radio than most other parts of the UK. The chart below (extracted directly from a recent Ofcom report) demonstrates that satisfaction with existing radio provision is almost evenly spread across the whole UK, but consumers in London and Northern Ireland are the least satisfied.
In summary, radio in the UK has been a victim of its own success. The universal availability of a range of both BBC and commercial ‘national’ stations, combined with the extensive choice of local stations available in most markets, mean that consumers are already relatively spoilt for choice on the analogue radio platform. There is very little unsatisfied demand for radio content because the UK already has such a comprehensive choice of radio content on offer. As a result, any new radio platform (DAB, satellite, online, etc) is going to find it hard to compete with the high quality and diverse choice of what is already on offer.
This was always going to make it tough for the DAB platform to entice consumers to purchase DAB receivers as anything other than a ‘replacement’ for their existing analogue radios. Unfortunately, the natural replacement cycle for radio receivers is so slow (maybe ten years or more) that it will never prove sufficient for a complete UK digital switchover to be co-ordinated for radio, as is happening in the television market. The UK has some of the best radio in the world – ironically, this has been our digital downfall.
Consumer demand for DAB radio receivers
As noted earlier, consumer demand for DAB hardware is largely a function of demand for DAB content. You will only want to buy a DAB radio if there is something interesting enough you want to listen to on the DAB platform.
Ofcom research demonstrates clearly the lack of interest amongst consumers in purchasing DAB radio receivers. In this year’s survey, only 16% of consumers (without a DAB radio) say they are likely to purchase a DAB radio within the next 12 months. Two years ago, 19% said they would be likely to purchase a DAB radio within the next 6 months. This is very bad news for manufacturers and retailers of DAB radios. Worse, this year not only do 64% of consumers say they are unlikely to purchase a DAB radio, but 20% say they don’t know – a demonstration that a DAB radio is far from being a ‘must have’ gadget on consumers’ wants lists.
The data for current levels of DAB radio receiver ownership are not very helpful in determining the demand for DAB radio receivers. The quarterly survey by RAJAR found in 2009 Q1 that 32.1% of adult respondents claimed to own a DAB radio. However, the annual Ofcom survey found in the same quarter that 41% of adult respondents claimed to have a DAB radio in their household. This disparity between the results from RAJAR and Ofcom would appear to be widening over time.
The uncertainty in the data regarding ownership levels of DAB receivers is not surprising, given the evident level of consumer confusion. Firstly, many radios on the market have the words “digital” or “digital radio” written on them, meaning that they either incorporate a digital clock (for radio alarm clocks) or that they offer ‘digital’ tuning of analogue wavebands, despite them not offering DAB reception. Secondly, the majority of 'DAB radios' presently on sale in the UK offer DAB reception in combination with analogue radio and/or internet radio. When DAB radio receivers were first introduced a decade ago, all the models offered were DAB-only. Nowadays, it is harder to find a DAB-only model in shops. Earlier this year, I surveyed the radio hardware on sale from UK retailers (see chart below) and found that the most common DAB consumer proposition is now an ‘FM + DAB’ radio.
In its latest consumer research on take-up of digital radio, Ofcom said that the result of its survey (see below) “highlights the continued lack of awareness among consumers of ways of accessing digital radio”. Consumers have low awareness of their ability to already access digital radio, and It appears that the words “digital radio”, “digital audio broadcasting” and “DAB” are not yet precisely understood. This uncertainty makes the results of market research about ownership levels of DAB radio hardware somewhat unreliable.
One of the targets set by the Digital Radio Working Group at the end of 2008 for the implementation of digital radio was that DAB radios should reach 50% of radio receiver sales by volume by the end of 2010. However, if the current rate of growth continues, this target is unlikely to be reached until 2016 (see chart below).
Besides, this target is largely irrelevant to digital switchover because it seems to assume that consumers are making a definitive choice between the purchase of a DAB radio or an analogue radio. In fact, as the earlier chart shows, the majority of DAB radios presently offered by retailers also include FM radio. Although the DRDB data states that 22% of radios sold in the UK incorporate DAB, the vast majority of those include FM too. So, for every 100 new radios sold, you are probably adding to the UK’s inventory of receivers between 95 and 98 new FM radios, at the same time as adding 22 new DAB radios. In other words, the household penetration level of analogue radio receivers is barely diminishing at all, a fact that will ensure that FM broadcasting remains as vital to our radio system as it has always been.
In summary, the DAB platform seems to be developing slowly as a supplementary platform to existing analogue radio reception. Far from DAB radios ‘replacing’ analogue radios, the overwhelming majority of new radios purchased in the UK are still analogue-only. The remainder are mostly DAB/analogue combination receivers. In this way, DAB has much in common with ‘Long Wave’ radio, where consumers for a long time were offered a choice of ‘FM+AM’ or FM+AM+Long Wave’ receivers in retail stores. Like Long Wave, for a minority of consumers DAB may be a ‘must have’ when purchasing a new radio, but for the majority it is merely an optional extra whose purchase is likely to be very dependent on the comparative prices of available options.
Conclusion
The publicly available data on the demand for DAB is not particularly encouraging for the platform’s future. Much of the implementation of DAB to date in the UK has focused on ‘supply-side’ issues, without seeming to determine whether there is sufficient demand from consumers for new content, and without determining whether that new content would prove sufficiently attractive to lure consumers into shops to purchase DAB radios. Ironically, it appears that if our existing system of analogue radio broadcasting had been less well developed in terms of both the range of available content and its near universal delivery, DAB might have been better able to address any pent-up demand from consumers. As it is, the majority of consumers seem very content with their existing radio options. Our pursuit of excellence in radio over the last 80 years has created something we can be proud of – but it has also made it hard for it to be bettered by a ‘new’ system such as DAB.
[For more data on the challenges facing digital radio in the UK, check out a presentation I made to the European Broadcasting Union Digital Radio Conference in June 2009]
10 Sept 2009
Funding DAB radio infrastructure upgrade: still 'no'

The Media Show, BBC Radio 4, 2 September 2009 @ 1330
Steve Hewlett interviewed Tim Davie, Director of BBC Audio & Music
We talked at the Radio Festival a few months ago and you talked a lot about DAB. The criteria have been stated now for moving forward to switchover, or before anyone contemplates switching off the analogue FM signal, of 50% of listening and 90%+ of coverage. Do you think that’s realistic by 2015?
I use the word ‘ambitious’ and I mean it. I think it’s tough. It is possible. I think the radio industry to date has shown an incremental path towards digital and, unless you get a big step change, you’ll never get there. And, to be fair, the BBC has driven this harder than anyone.
When we last spoke about it, there was a discussion of £100m or so being needed to pay for the rollout of not the BBC stuff but whatever is necessary for the commercial sector to go digital. At that time, I asked you specifically whether there was any money in your budget identified for that purpose and you said ‘no’. Has anything changed since we last spoke?
It’s another ‘no’. No, nothing has changed and until the plan ….
This is not going to happen, is it?
I think that radio will move to digital, and I think that ….
Will it be DAB?
I think at this point, it will be …. I believe in DAB. I say ‘at this point’ because I think we have hurdles to jump over.
Steve Hewlett interviewed Tim Davie, Director of BBC Audio & Music
We talked at the Radio Festival a few months ago and you talked a lot about DAB. The criteria have been stated now for moving forward to switchover, or before anyone contemplates switching off the analogue FM signal, of 50% of listening and 90%+ of coverage. Do you think that’s realistic by 2015?
I use the word ‘ambitious’ and I mean it. I think it’s tough. It is possible. I think the radio industry to date has shown an incremental path towards digital and, unless you get a big step change, you’ll never get there. And, to be fair, the BBC has driven this harder than anyone.
When we last spoke about it, there was a discussion of £100m or so being needed to pay for the rollout of not the BBC stuff but whatever is necessary for the commercial sector to go digital. At that time, I asked you specifically whether there was any money in your budget identified for that purpose and you said ‘no’. Has anything changed since we last spoke?
It’s another ‘no’. No, nothing has changed and until the plan ….
This is not going to happen, is it?
I think that radio will move to digital, and I think that ….
Will it be DAB?
I think at this point, it will be …. I believe in DAB. I say ‘at this point’ because I think we have hurdles to jump over.
Digital radio: Parliamentary Question
House of Commons: Written Ministerial Statements: 9 September 2009
Digital Broadcasting: Radio
Tim Farron: To ask the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport whether his Department’s proposals for the analogue radio switch-off in 2015 have been submitted for rural proofing to the (a) Commission for Rural Communities and (b) Rural Advocate.
Mr. Simon: The Digital Britain White Paper set out our commitment to a full impact assessment of the Digital Radio Upgrade; including consideration of the rural impact. To inform these assessments we will work closely with the relevant stakeholders, such as the Commission for Rural Communities and the Rural Advocate.
Tim Farron: To ask the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport what assessment he has made of the merits of providing financial assistance to (a) low-income households and (b) households in hilly rural areas in respect of the analogue radio switch-off in 2015.
Mr. Simon: The Digital Britain White Paper set out our commitment to conduct a full impact assessment, including a cost benefit analysis of DigitalRadio Upgrade. The results of this impact assessment will help determine whether there is a case for a Digital Radio Help Scheme, and if so, what its scope would be. In addition, the Consumer Expert Group, which brought together key consumer representatives to inform the Digital TV switchover process, has been invited to extend its scope to cover radio and will ensure that the Digital Radio Upgrade programme takes account of the wide range of listener needs.
Digital Broadcasting: Radio
Tim Farron: To ask the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport whether his Department’s proposals for the analogue radio switch-off in 2015 have been submitted for rural proofing to the (a) Commission for Rural Communities and (b) Rural Advocate.
Mr. Simon: The Digital Britain White Paper set out our commitment to a full impact assessment of the Digital Radio Upgrade; including consideration of the rural impact. To inform these assessments we will work closely with the relevant stakeholders, such as the Commission for Rural Communities and the Rural Advocate.
Tim Farron: To ask the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport what assessment he has made of the merits of providing financial assistance to (a) low-income households and (b) households in hilly rural areas in respect of the analogue radio switch-off in 2015.
Mr. Simon: The Digital Britain White Paper set out our commitment to conduct a full impact assessment, including a cost benefit analysis of DigitalRadio Upgrade. The results of this impact assessment will help determine whether there is a case for a Digital Radio Help Scheme, and if so, what its scope would be. In addition, the Consumer Expert Group, which brought together key consumer representatives to inform the Digital TV switchover process, has been invited to extend its scope to cover radio and will ensure that the Digital Radio Upgrade programme takes account of the wide range of listener needs.
8 Sept 2009
EU Commissioner Viviane Reding: digital radio in Europe
Interview from the latest issue of Germany’s Meinungsbarometer Digitaler Rundfunk magazine:
EU COMMISSIONER OPPOSES EUROPEAN RADIO LEGISLATION
Equipment manufacturers and broadcasters must promote standardisation
In light of the national debate about digital radio [in Germany], EU Commissioner for Information & Media, Viviane Reding, in an interview with Meinungsbarometer Digital Broadcasting, has called for receiver manufacturers and content providers to implement compatible standards. This would ensure that, in most EU Member States, the family of DAB standards are either already being used or would be introduced. If the trend towards hybrid media devices continues, the EU Commissioner believes there is no need for statutory regulation.
Ms Reding, millions of European motorists make cross-border journeys and are subject to various digital terrestrial radio standards. What is the EU doing to achieve a unified standard for digital terrestrial radio in Europe?
This issue of EU-wide radio standardisation is still in its infancy. The main reason is that radio, from a political, business and consumer standpoint, is organised primarily as a regional or even local product. This is, in principle, rightly so. The reason the radio landscape in Europe is so fascinating is because it is so diverse and highly innovative. Therefore, EU-wide radio legislation is not advocated.
Standardisation, however, is still an issue during the transition to digital radio reception. The market is making considerable progress on this question. Currently, the DAB standard is the most widely used digital terrestrial radio technology in the Member States of the EU. DAB is already used in Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Spain, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Sweden and the UK. Malta is already using the newer DAB+ standard, and its implementation is currently also being considered in Germany. Later this year, France and the Netherlands want to test another new standard, DMB, for digital terrestrial radio broadcasting.
I hope that, in the interest of tourists and cross-border travellers, that device manufacturers and content providers here will soon agree with each other to use a standard or at least open, compatible standards. I therefore welcome the fact that device manufacturers are increasingly coming to market with products, at little additional cost, that can process several standards and codecs. If this positive development continues, a statutory standardisation will certainly not be necessary.
In Germany, there are moves to postpone the 2015 date for the planned closure of FM. How do you see this situation developing in other European countries?
I believe the time is not ripe for a single EU-wide radio FM switchoff, such as we are doing for analogue TV in 2012. I can also well imagine that the 27 EU Member States, given their different levels of development, will want to take their own innovative approaches to digital radio switchover. Therefore, it is important from the perspective of the EU that the Member States take into account in their plans what their neighbours - and beyond – have done and learn from others’ good and less good experiences. The European Commission is strongly promoting these individual views and experiences at a European level.
As for financing the construction of the infrastructure for new digital terrestrial audio broadcasting: can you envisage the Digital Dividend being used?
The digital dividend is defined as the spectrum freed by the shutdown of analogue broadcasting once all programmes are only broadcast digitally. The term "digital dividend" is therefore not a direct means with which one can finance digital radio networks, as it only creates efficiency gains through technical progress. The digital dividend in the medium of terrestrial radio is significantly lower than in terrestrial television where, through appropriate co-ordination at the European level, the potential economic benefits of the digital dividend between 2009 and 2015 will create an additional 20 to 50 billion Euros. With terrestrial radio, however, the digital dividend could be higher, depending on the performance of digital transmission standards that are replacing analogue FM. In my view, this is the strongest incentive for a shift to digital terrestrial radio broadcasting.
EU COMMISSIONER OPPOSES EUROPEAN RADIO LEGISLATION
Equipment manufacturers and broadcasters must promote standardisation
In light of the national debate about digital radio [in Germany], EU Commissioner for Information & Media, Viviane Reding, in an interview with Meinungsbarometer Digital Broadcasting, has called for receiver manufacturers and content providers to implement compatible standards. This would ensure that, in most EU Member States, the family of DAB standards are either already being used or would be introduced. If the trend towards hybrid media devices continues, the EU Commissioner believes there is no need for statutory regulation.
Ms Reding, millions of European motorists make cross-border journeys and are subject to various digital terrestrial radio standards. What is the EU doing to achieve a unified standard for digital terrestrial radio in Europe?
This issue of EU-wide radio standardisation is still in its infancy. The main reason is that radio, from a political, business and consumer standpoint, is organised primarily as a regional or even local product. This is, in principle, rightly so. The reason the radio landscape in Europe is so fascinating is because it is so diverse and highly innovative. Therefore, EU-wide radio legislation is not advocated.
Standardisation, however, is still an issue during the transition to digital radio reception. The market is making considerable progress on this question. Currently, the DAB standard is the most widely used digital terrestrial radio technology in the Member States of the EU. DAB is already used in Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Spain, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Sweden and the UK. Malta is already using the newer DAB+ standard, and its implementation is currently also being considered in Germany. Later this year, France and the Netherlands want to test another new standard, DMB, for digital terrestrial radio broadcasting.
I hope that, in the interest of tourists and cross-border travellers, that device manufacturers and content providers here will soon agree with each other to use a standard or at least open, compatible standards. I therefore welcome the fact that device manufacturers are increasingly coming to market with products, at little additional cost, that can process several standards and codecs. If this positive development continues, a statutory standardisation will certainly not be necessary.
In Germany, there are moves to postpone the 2015 date for the planned closure of FM. How do you see this situation developing in other European countries?
I believe the time is not ripe for a single EU-wide radio FM switchoff, such as we are doing for analogue TV in 2012. I can also well imagine that the 27 EU Member States, given their different levels of development, will want to take their own innovative approaches to digital radio switchover. Therefore, it is important from the perspective of the EU that the Member States take into account in their plans what their neighbours - and beyond – have done and learn from others’ good and less good experiences. The European Commission is strongly promoting these individual views and experiences at a European level.
As for financing the construction of the infrastructure for new digital terrestrial audio broadcasting: can you envisage the Digital Dividend being used?
The digital dividend is defined as the spectrum freed by the shutdown of analogue broadcasting once all programmes are only broadcast digitally. The term "digital dividend" is therefore not a direct means with which one can finance digital radio networks, as it only creates efficiency gains through technical progress. The digital dividend in the medium of terrestrial radio is significantly lower than in terrestrial television where, through appropriate co-ordination at the European level, the potential economic benefits of the digital dividend between 2009 and 2015 will create an additional 20 to 50 billion Euros. With terrestrial radio, however, the digital dividend could be higher, depending on the performance of digital transmission standards that are replacing analogue FM. In my view, this is the strongest incentive for a shift to digital terrestrial radio broadcasting.
7 Sept 2009
UK Commercial radio revenues Q2 2009
Commercial radio revenue figures for 2009’s second quarter have been published.
Q1 2009 DATA
£119.7m total revenues – lowest since Q3 1999
£34.8m local revenues – lowest since Q1 2001
£60.0m national revenues – lowest since Q1 1998
£24.8m branded content
YEAR-ON-YEAR
Total revenues – down 10.8%
Local revenues – down 6.0%
National revenues – down 16.1%
Branded content – down 3.7%
QUARTER-ON-QUARTER
Total revenues – down 6.9%
Local revenues – down 5.4%
National revenues – down 12.3%
Branded content – up 6.0%

FOUR-QUARTER MOVING AVERAGE DATA
£514.6m total revenues
Down 13.4% year-on-year (last quarter: down 13.1% year-on-year)

Whatever may be going on elsewhere in the economy, it is hard to see any green shoots of recovery in the UK commercial radio …. yet. Total revenues in Q2 2009 fell by 10.8% year-on-year to £119.7m. Initially, this might look mildly positive compared to the 19.5% year-on-year fall experienced last quarter. But remember that the downturn in UK radio first hit in Q2 2008 and had already reduced that quarter’s revenues 10.1% year-on-year. As a result, Q2 revenues in 2009 are now 20% below what they had been two years ago, a decline so significant that it will prove difficult to recapture even when the economy does improve.
National advertisers remain the weak spot for UK commercial radio, with revenues in Q2 2009 down 16.1% year-on-year. But once again, Q2 in 2008 was the start of the downturn and that quarter showed a 15.9% fall year-on-year. National revenues in Q2 2009 are now 29% below what they had been two years ago. It will be a mighty challenge to recoup such losses.
The notion that UK commercial radio is merely experiencing a cyclical blip and will quickly show recovery once the overall economy improves is a great feelgood story, but one that is not supported by the industry’s own data. Long before the ‘credit crunch’ hit us all, UK commercial radio revenues were already showing structural decline, a trend that the current economic cycle has merely exacerbated.
Nothing demonstrates the long-term trend more starkly than a glance at the year-on-year changes to commercial radio’s total revenues in recent quarters. Of the last 20 quarters, only 7 have demonstrated year-on-year revenue growth (one quarter in 2004, one quarter in 2005, one quarter in 2006, three quarters in 2007 and one quarter in 2008). The most recent quarter’s total revenues were 29% below the peak achieved as long ago as Q4 2003. If these comparisons were adjusted for the effects of inflation, the decline would look even more stark.

For the commercial radio industry, business will never be the same again. The ‘goldrush’ 1990s are never going to happen again, at least not without some kind of radio revolution (such as the BBC wilfully destroying Radio Two’s popularity, as they did with Radio One in the early 1990s). As a result, the commercial radio industry will need to change its modus operandi more substantially than ever before, not to thrive, but in order simply to survive. If it doesn’t change, we won’t have much of a commercial radio industry left at all.
The seemingly widely held belief that commercial radio MUST continue to exist in its present form because it is a highly regulated and licensed industry is simply false. If there was one lesson that should have been learnt from the implementation of DAB radio in the UK, it was that ensuring that a small group of commercial interests control a technology and the access to it counts for nothing if there is almost no demand for it. With DAB, radio broadcasting groups got what they wanted – their cartel became the licensed gatekeeper and owner of DAB. But if nobody wants your DAB, you are left being gatekeeper to a field of nothing.
It’s the same with commercial radio. If advertisers and listeners don’t want your product, there is no reason for it to exist, regardless of you waving around your scarce Ofcom licence. Not so long ago, station owners could still foist crappy radio content on the public because listeners were starved of alternatives, but digital audio and the internet have changed that FOREVER. No longer is there any market for second-rate radio. And, in commercial radio, if unwanted or irrelevant content doesn’t attract listeners, it won’t last long.
In this context, the latest Ofcom radioconsultation (“Radio: the implications of Digital Britain for localness regulation”) is a remarkably disappointing document. At a time when commercial radio is at a crossroads in so many senses (profitability, consolidation, platforms, localness, public service, interactivity, CPM, etc), this latest chapter in Ofcom’s many attempts to map out “The Future Of Radio” is no more than tinkering at the edges of existing radio regulation.
What was needed was a full-blown, courageous effort to overhaul the radio regulatory system in order to ensure that commercial radio continues to exist financially and that the diminishing number of licensees genuinely serves the public’s articulated radio needs. Instead, we have an Ofcom consultation that is no more than a grudging reaction to Lord Carter’s Digital Britain proposals, some of which are now adopted as if they were Ofcom’s own, some of which are watered down, and some of which have been ignored altogether.
The reluctance drips from every page. There are 81 uses of the word ‘if’ in this 82-page document. Almost every one of its proposals is tainted with uncertainty – “if and when new legislation is passed” or “if Parliament decides not to take forward”. Rather than seizing the opportunities that arise from the painful ‘crossroads’ when change is an inevitable necessity rather than a nicety, Ofcom seems happy to sit in the back seat and respond “whatever!” to ideas it receives, rather than grabbing at innovation and pushing it forward. It reads very much as if written by nobody who has ever themselves run a commercial business where painful life and death decisions have to be made, sometimes at breakneck speed and often without the aid of a parachute.
Ofcom continues to treat the commercial radio industry like a naughty child who, although 36 years of age now, cannot be trusted with more than a five pound note. Every Ofcom proposal continues to keep its centralised, London-based decision making about local commercial radio firmly within its own control, without trusting licensees to co-regulate in any meaningful way. For example:
· Proposal 1 requires stations to submit a request every occasion they seek a change
· Proposal 2 will lead to “a short consultation upon receipt of such a request”
· Proposal 3 requires stations to submit a request every occasion they seek a change
· Proposal 4 will lead to “a short consultation in most cases”
· Proposal 5 will lead to “short consultations in most cases”.
Only one thing is certain – Ofcom will be drowning in consultations for the foreseeable future. These five proposals alone (out of eight) multiplied by 300 stations plus DAB multiplexes yields a potential 1,000+ new consultations or requests. And yet the document claims that these Ofcom proposals are “broadly deregulatory”.
Sadly, more than anything else, the Ofcom document completely lacks any kind of vision as to what the commercial radio landscape might look like in the future, the antithesis of what the Digital Britain consultation exercise was trying to achieve. This is a missed opportunity for Ofcom. Not just this latest document, but in 2009 when the whole “what is the future of radio?” debate is probably at the most critical point in commercial radio’s history. It appears to many in the industry that Ofcom has simply disengaged from radio. This is a particular irony for an industry that prides itself on its success in one-to-one communication.
It may seem a stupid question……. If Ofcom still sees itself as the party with the skills necessary to make 1,000 potential individual decisions on the future of individual commercial radio stations, how is commercial radio presently in such a sad state of affairs as a result (partly) of previous regulatory decisions? We tend to respect and trust people who can demonstrate a positive track record. Why would I let a doctor operate on me who had killed almost every patient he had ever consulted?
Q1 2009 DATA
£119.7m total revenues – lowest since Q3 1999
£34.8m local revenues – lowest since Q1 2001
£60.0m national revenues – lowest since Q1 1998
£24.8m branded content
YEAR-ON-YEAR
Total revenues – down 10.8%
Local revenues – down 6.0%
National revenues – down 16.1%
Branded content – down 3.7%
QUARTER-ON-QUARTER
Total revenues – down 6.9%
Local revenues – down 5.4%
National revenues – down 12.3%
Branded content – up 6.0%

FOUR-QUARTER MOVING AVERAGE DATA
£514.6m total revenues
Down 13.4% year-on-year (last quarter: down 13.1% year-on-year)

Whatever may be going on elsewhere in the economy, it is hard to see any green shoots of recovery in the UK commercial radio …. yet. Total revenues in Q2 2009 fell by 10.8% year-on-year to £119.7m. Initially, this might look mildly positive compared to the 19.5% year-on-year fall experienced last quarter. But remember that the downturn in UK radio first hit in Q2 2008 and had already reduced that quarter’s revenues 10.1% year-on-year. As a result, Q2 revenues in 2009 are now 20% below what they had been two years ago, a decline so significant that it will prove difficult to recapture even when the economy does improve.
National advertisers remain the weak spot for UK commercial radio, with revenues in Q2 2009 down 16.1% year-on-year. But once again, Q2 in 2008 was the start of the downturn and that quarter showed a 15.9% fall year-on-year. National revenues in Q2 2009 are now 29% below what they had been two years ago. It will be a mighty challenge to recoup such losses.
The notion that UK commercial radio is merely experiencing a cyclical blip and will quickly show recovery once the overall economy improves is a great feelgood story, but one that is not supported by the industry’s own data. Long before the ‘credit crunch’ hit us all, UK commercial radio revenues were already showing structural decline, a trend that the current economic cycle has merely exacerbated.
Nothing demonstrates the long-term trend more starkly than a glance at the year-on-year changes to commercial radio’s total revenues in recent quarters. Of the last 20 quarters, only 7 have demonstrated year-on-year revenue growth (one quarter in 2004, one quarter in 2005, one quarter in 2006, three quarters in 2007 and one quarter in 2008). The most recent quarter’s total revenues were 29% below the peak achieved as long ago as Q4 2003. If these comparisons were adjusted for the effects of inflation, the decline would look even more stark.

For the commercial radio industry, business will never be the same again. The ‘goldrush’ 1990s are never going to happen again, at least not without some kind of radio revolution (such as the BBC wilfully destroying Radio Two’s popularity, as they did with Radio One in the early 1990s). As a result, the commercial radio industry will need to change its modus operandi more substantially than ever before, not to thrive, but in order simply to survive. If it doesn’t change, we won’t have much of a commercial radio industry left at all.
The seemingly widely held belief that commercial radio MUST continue to exist in its present form because it is a highly regulated and licensed industry is simply false. If there was one lesson that should have been learnt from the implementation of DAB radio in the UK, it was that ensuring that a small group of commercial interests control a technology and the access to it counts for nothing if there is almost no demand for it. With DAB, radio broadcasting groups got what they wanted – their cartel became the licensed gatekeeper and owner of DAB. But if nobody wants your DAB, you are left being gatekeeper to a field of nothing.
It’s the same with commercial radio. If advertisers and listeners don’t want your product, there is no reason for it to exist, regardless of you waving around your scarce Ofcom licence. Not so long ago, station owners could still foist crappy radio content on the public because listeners were starved of alternatives, but digital audio and the internet have changed that FOREVER. No longer is there any market for second-rate radio. And, in commercial radio, if unwanted or irrelevant content doesn’t attract listeners, it won’t last long.
In this context, the latest Ofcom radio
What was needed was a full-blown, courageous effort to overhaul the radio regulatory system in order to ensure that commercial radio continues to exist financially and that the diminishing number of licensees genuinely serves the public’s articulated radio needs. Instead, we have an Ofcom consultation that is no more than a grudging reaction to Lord Carter’s Digital Britain proposals, some of which are now adopted as if they were Ofcom’s own, some of which are watered down, and some of which have been ignored altogether.
The reluctance drips from every page. There are 81 uses of the word ‘if’ in this 82-page document. Almost every one of its proposals is tainted with uncertainty – “if and when new legislation is passed” or “if Parliament decides not to take forward”. Rather than seizing the opportunities that arise from the painful ‘crossroads’ when change is an inevitable necessity rather than a nicety, Ofcom seems happy to sit in the back seat and respond “whatever!” to ideas it receives, rather than grabbing at innovation and pushing it forward. It reads very much as if written by nobody who has ever themselves run a commercial business where painful life and death decisions have to be made, sometimes at breakneck speed and often without the aid of a parachute.
Ofcom continues to treat the commercial radio industry like a naughty child who, although 36 years of age now, cannot be trusted with more than a five pound note. Every Ofcom proposal continues to keep its centralised, London-based decision making about local commercial radio firmly within its own control, without trusting licensees to co-regulate in any meaningful way. For example:
· Proposal 1 requires stations to submit a request every occasion they seek a change
· Proposal 2 will lead to “a short consultation upon receipt of such a request”
· Proposal 3 requires stations to submit a request every occasion they seek a change
· Proposal 4 will lead to “a short consultation in most cases”
· Proposal 5 will lead to “short consultations in most cases”.
Only one thing is certain – Ofcom will be drowning in consultations for the foreseeable future. These five proposals alone (out of eight) multiplied by 300 stations plus DAB multiplexes yields a potential 1,000+ new consultations or requests. And yet the document claims that these Ofcom proposals are “broadly deregulatory”.
Sadly, more than anything else, the Ofcom document completely lacks any kind of vision as to what the commercial radio landscape might look like in the future, the antithesis of what the Digital Britain consultation exercise was trying to achieve. This is a missed opportunity for Ofcom. Not just this latest document, but in 2009 when the whole “what is the future of radio?” debate is probably at the most critical point in commercial radio’s history. It appears to many in the industry that Ofcom has simply disengaged from radio. This is a particular irony for an industry that prides itself on its success in one-to-one communication.
It may seem a stupid question……. If Ofcom still sees itself as the party with the skills necessary to make 1,000 potential individual decisions on the future of individual commercial radio stations, how is commercial radio presently in such a sad state of affairs as a result (partly) of previous regulatory decisions? We tend to respect and trust people who can demonstrate a positive track record. Why would I let a doctor operate on me who had killed almost every patient he had ever consulted?
2 Sept 2009
DAB radio European update
NORWAY
The newspaper Aftenposten reported that “sales of DAB receivers are still at a snail’s pace”, with only 61,000 sold in Norway in 2008, compared to eight times that number of analogue receivers sold. Culture Minister Trond Giske said that, if his party wins the election this autumn, “we will present a white paper on DAB in 2010 which, amongst other issues, will discuss whether the government can contribute more actively to promote the digital migration of the radio medium. We now have good experience from the digital migration of television, though the radio medium will take longer and require more preparation. Among other things, there are many more radio receivers to be replaced than there were TV sets, so it is extremely important that this transition occurs at a socially acceptable pace.”
The following day, in an article headlined “Poor Sales Of DAB Radios”, Norway’s Kampanje magazine reported that sales of DAB radios are only 40,000 to 60,000 per annum out of a total 700,000 to 800,000 radios sold annually. Cumulatively, over the last decade, 300,000 to 400,000 DAB radios have been sold out of a total 8,000,000 radio receivers. Synnove Bjoke, managing director of electronics trade organisation Elektronikkbransjen, said: “We believe sales will increase in the years ahead. The day we are given a [FM] switch-off date, we will sell many more DAB radios, but we need a date. There has been uncertainty amongst people, and also in our industry, as to whether we’re ever going to switch off the FM band, and that uncertainty makes people buy regular FM radios.”
SWITZERLAND
Speaking at Swiss Radio Day 2009 held in Zurich last week, Swiss Radio German-language station DRS director Walter Ruegg announced the introduction of DAB broadcasts from 15 October and said that the platform would also be made available to local commercial stations in Switzerland. English-language public station World Radio Switzerland will also be broadcast nationally on DAB from the same date.
IRELAND
RTE Radio boss Clare Duigan told the Irish Independent newspaper that the absence of commercial stations on the DAB platform was a “big issue”. She said: "We've begun to talk to the Independent Broadcasters of Ireland [IBI] and we're very much hopeful that over the next couple of months we'll be able to work something out. DAB is one of those areas where we really need to work together as an industry." But IBI boss Willie O’Reilly responded that commercial stations are not interested in rejoining the DAB platform “at the moment” because “the return on investment looks poor”. UTV head of Irish radio Ronan McManamy said that DAB is “not a priority” for UTV in the “current marketplace”.
The newspaper Aftenposten reported that “sales of DAB receivers are still at a snail’s pace”, with only 61,000 sold in Norway in 2008, compared to eight times that number of analogue receivers sold. Culture Minister Trond Giske said that, if his party wins the election this autumn, “we will present a white paper on DAB in 2010 which, amongst other issues, will discuss whether the government can contribute more actively to promote the digital migration of the radio medium. We now have good experience from the digital migration of television, though the radio medium will take longer and require more preparation. Among other things, there are many more radio receivers to be replaced than there were TV sets, so it is extremely important that this transition occurs at a socially acceptable pace.”
The following day, in an article headlined “Poor Sales Of DAB Radios”, Norway’s Kampanje magazine reported that sales of DAB radios are only 40,000 to 60,000 per annum out of a total 700,000 to 800,000 radios sold annually. Cumulatively, over the last decade, 300,000 to 400,000 DAB radios have been sold out of a total 8,000,000 radio receivers. Synnove Bjoke, managing director of electronics trade organisation Elektronikkbransjen, said: “We believe sales will increase in the years ahead. The day we are given a [FM] switch-off date, we will sell many more DAB radios, but we need a date. There has been uncertainty amongst people, and also in our industry, as to whether we’re ever going to switch off the FM band, and that uncertainty makes people buy regular FM radios.”
SWITZERLAND
Speaking at Swiss Radio Day 2009 held in Zurich last week, Swiss Radio German-language station DRS director Walter Ruegg announced the introduction of DAB broadcasts from 15 October and said that the platform would also be made available to local commercial stations in Switzerland. English-language public station World Radio Switzerland will also be broadcast nationally on DAB from the same date.
IRELAND
RTE Radio boss Clare Duigan told the Irish Independent newspaper that the absence of commercial stations on the DAB platform was a “big issue”. She said: "We've begun to talk to the Independent Broadcasters of Ireland [IBI] and we're very much hopeful that over the next couple of months we'll be able to work something out. DAB is one of those areas where we really need to work together as an industry." But IBI boss Willie O’Reilly responded that commercial stations are not interested in rejoining the DAB platform “at the moment” because “the return on investment looks poor”. UTV head of Irish radio Ronan McManamy said that DAB is “not a priority” for UTV in the “current marketplace”.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)